Electrophysiology
Your heart has an electrical system that keeps it beating in a steady rhythm, but if those signals go awry, you can develop unpleasant symptoms and dramatically increase your risk for serious problems such as stroke. At Riverside Heart & Vascular Institute, our electrophysiologists (EPs) are here to help get your heart back in the right rhythm with cutting-edge treatments for common arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation (A-Fib).
To request an appointment close to home, call (844) 404-4787 or fill out our quick form. Or, find a Riverside arrhythmia specialist anytime online:
Medications
People with A-fib have an increased risk for strokes, so getting your heartbeat back on track is essential to reduce your risks. Your doctor may prescribe one of several different medications, especially if your symptoms are mild. Because there’s no cure for A-fib, these medications need to be taken indefinitely. These may include:
- Blood thinners, or anticoagulants, to prevent the formation of blood clots in the heart, which increase the risk of strokes
- Medications such as beta blockers, calcium channel blockers and digoxin, which slow your heart rate to improve symptoms
- Medications that restore your heart’s natural rhythm, including sodium channel blockers and potassium channel blockers
Catheter Ablation
As an alternative to taking medication for life, or if medications fail to control your heart rhythm, the next step may be to undergo catheter ablation. In this procedure, one of our electrophysiologists uses a device to destroy small areas of heart tissue that may be causing abnormal heartbeat. The two most commonly used devices in catheter ablation use heat (radiofrequency) or cold energy (cryoablation) to eliminate cardiac tissue.
Pacemaker
Patients who suffer from an abnormally slow heart rate cab now receive the world’s smallest pacemaker at Riverside Heart & Vascular Institute. Our electrophysiology specialists can implant the Micra® Transcatheter Pacing System (TPS) heart device, which used the most advanced pacing technology at one-tenth the size of a traditional pacemaker and is approved for Medicare reimbursement. Pacemakers are the most common way to treat a slow heartbeat, restoring the heart’s normal heart rate and relieving symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath and fainting.
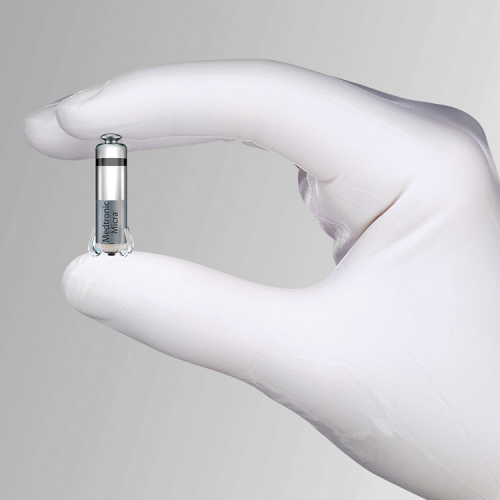
Micra Transcatheter Pacing System
Brad Suprenant, DO talks about the World’s Smallest Pacemaker, the Micra Transcatheter Pacing System (TPS). Now Available to Riverside Patients.
Listen to The PodcastIf your doctor determines that your heart’s ventricles (lower chambers) are not working in harmony, then you may be a candidate for a special device known as a biventricular pacemaker. Getting the ventricles in sync increases the heart’s output of blood. This treatment is known as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
The ICD, also an implanted device, is slightly larger than a pacemaker and works in a similar way. However, the ICD can send a low-energy shock that resets an abnormal heartbeat back to normal. It can also send a high-energy shock if an arrhythmia becomes so severe that the heart can't pump at all.
Combination Device
Your doctor may recommend a device that pairs a pacemaker and ICD in one unit.
Cardioversion
Like the electrical shocks to the heart that save lives in emergency situations, this elective procedure is sometimes used to help control symptoms in patients with A-fib.

Meet Our Team
Riverside's nationally recognized physicians specialize in the prevention, detection

